The index.html file is the default HTML file that opens in your browser when you visit any given directory on a web server.
In other words, index.html is the expected name of your website’s homepage, as well as the homepages of its individual subdomains and subdirectories.
It isn’t required to have an index.html file in your server’s public HTML directory. However, visitors will see a list of files when they visit your domain name (or any of the subdomains and subdirectories on it) if you don’t.
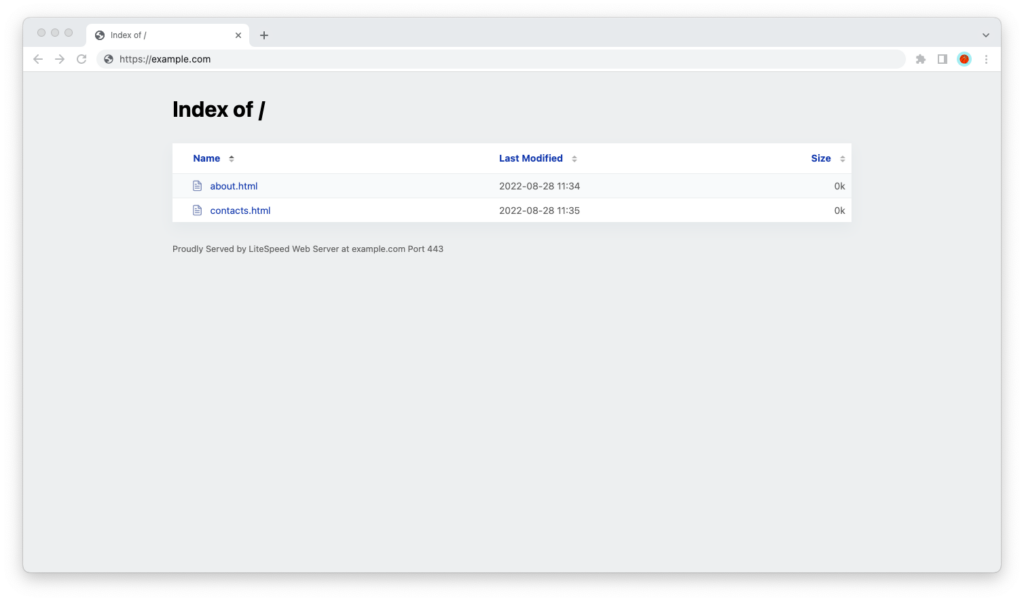
However you look at it, this isn’t a great user experience!
So unless you want your website to look like an FTP server from the 2000s, make sure there’s an index.html file in the public HTML directory.
Why Do We Use Index.html?
To give you the long answer short, because it’s how we tell browsers which HTML file in the directory to open by default.
When you type a URL in your browser’s address bar and press Enter on the keyboard, the browser performs a DNS lookup and finds the IP address of the server that the domain name in the URL points to.
Your browser then connects to the server and requests the contents of the directory in the page path of the URL. If there’s an index.html file in that directory, the server will return its contents to the browser. If there isn’t one, the server will typically show a list of files in the directory.
Why Is It Called Index.html?
In book publishing, the index is a guide through the book that allows you to navigate to the word or term you’re looking for.
Similarly, the index.html file is supposed to contain the home page of a website or web directory that allows the user to navigate to all other pages in an easy way.
It’s the starting point of the user’s journey on your website.

