Auto-tagging is a feature of Google Ads that automatically appends the landing page links of your ads with a URL parameter, called Google Click ID (GLCID), for ad tracking and campaign attribution.
The GLCID parameter is recognized by Google Analytics and Google Optimize, allowing you to attribute conversions to your ads and run A/B tests or personalize its content based on your Ads account, ad groups, campaigns, and keywords.
With auto-tagging, you no longer need to create and add UTM parameters to the final URLs of your ads. Auto-tagging also provides richer data in Google Analytics. This saves time and creates benefits for Google Ads users, especially those who run a lot of ads, such as ad agencies and large media buyers.
How to Enable Auto-Tagging
When you link your Google Ads account to your Google Analytics property, Google will enable auto-tagging for your Google Ads account by default.
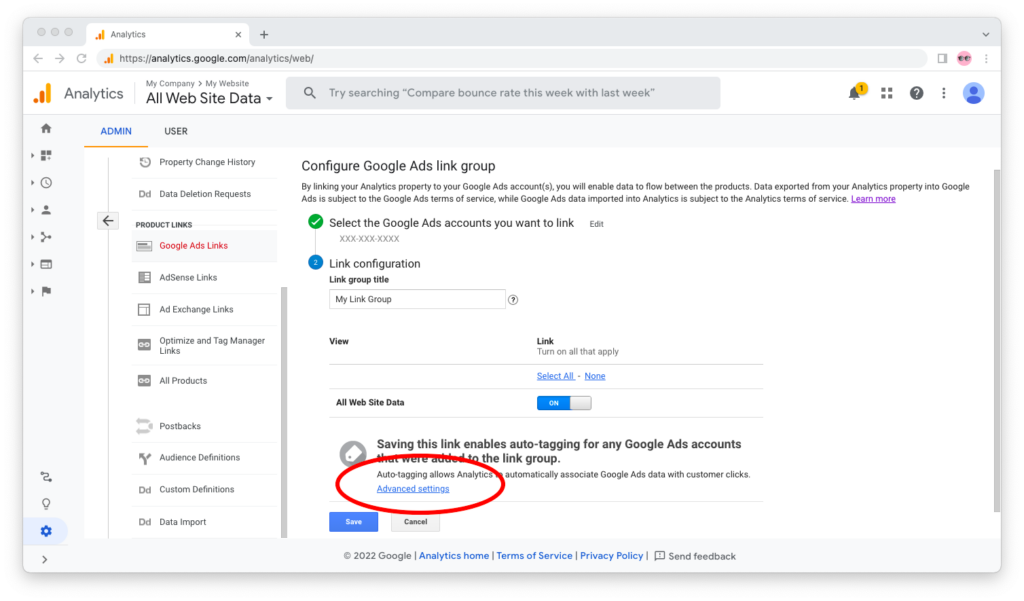
You can verify that this is the case by signing into Google Analytics, clicking on the gear icon in the bottom left corner to open the Admin tab, and then opening your property’s settings and navigating to “Google Ads Links” under “Product Links.”
Click on the “Advanced settings” link:
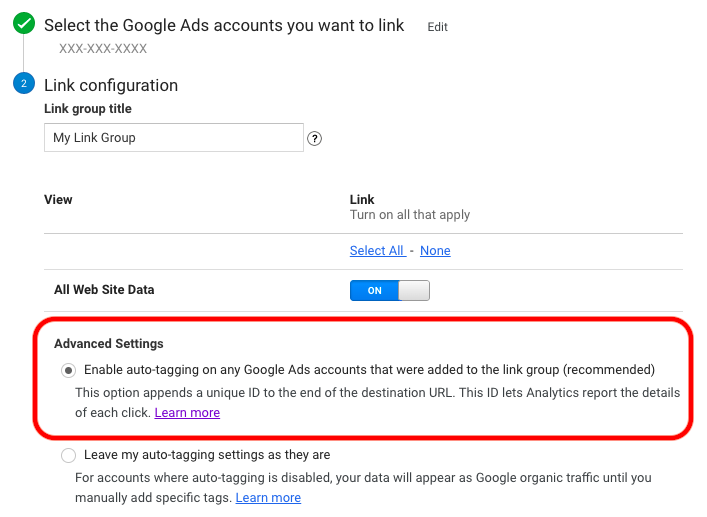
Under “Advanced Settings,” you want to make sure that you’ve selected the radio button “Enable auto-tagging on any Google Ads accounts that were added to the link group (recommended).”
GLCID vs. UTM Parameters
Google Click ID (GLCID) is a single URL parameter appended automatically to the final URL of every ad in Google Ads accounts with auto-tagging enabled.
If you use auto-tagging in your Google Ads account and as long as GLCID parameters are being added to the final URLs of your ads, you don’t need to add UTM parameters to them.
The GLCID parameter looks like this:
https://example.com?gclid=123xyz
Urchin Tracking Module (UTM) are a set of URL parameters that ad buyers must create and manually add to the final URL of every ad in Google Ads accounts with auto-tagging disabled.
UTM parameters look like this:
https://example.com?https://example.com?utm_source=x&utm_medium=y&utm_campaign=z&utm_id=123
Both the GLCID and UTM parameters are used for ad tracking and campaign attribution for your Google Ads traffic in Google Analytics. The difference is that GLCID is appended to your ads’ links automatically, whereas UTM parameters are parameters that you need to create and add manually.
Although it may seem that UTM parameters provide more comprehensive data because they are longer than the GLCID parameter, the opposite is true. When you use auto-tagging, you get richer data than when you manually tag your final URLs because you benefit from the integrations between Google Ads and Google Analytics under the hood.
In addition to the custom dimensions for campaign, source, medium, content, and term captured in Google Analytics by otherwise manually adding UTM parameters, auto-tagging provides you with data on:
- Query match type
- Ad distribution network
- Placement domain
- Ad group
- Ad format
- Final URL
Generally, Google recommends using auto-tagging in your Google Ads accounts because it saves you time and provides richer data. Only revert to manual tagging if, for one reason or another, it is necessary.
Helpful Links
The following pages in Google Ads’ Help Center can help you learn more about auto-tagging:

